Ensure that patient and health care provider safety standards are met during this procedure including:
Risk assessment and appropriate PPE
4 Moments of Hand Hygiene
Procedural Safety Pause is performed
Two patient identification
Safe patient handling practices
Biomedical waste disposal policies
Sharps handling
PROCEDURE
1.Obtain Order
Verify there is an order, protocol or medical directive to support the collection of blood. Document reason for enacting a medical directive.
Order laboratory tests in OneChart and obtain labels and follow steps to closed loop laboratory sample collection.
Check labels with patient's armband at bedside to verify patient, test and label is correct.
Blood drawing from indwelling arterial or central venous lines is done through a stopcock with a needleless access device on the sampling port.
Change the ethanol Swab Cap(TM) cap after each access. Draw blood sample through the needless access cap. Change this cap if if is contaminated or has residual blood.
2.Obtain Equipment
Perform hand hygiene before donning non-sterile gloves.
Assess risk for need of a face shield
Collect necessary equipment:
Vacutainer with luer lock adapter and needle
New ethanol based access cap
Blood collection tubes as required for ordered lab tests
Blood gas syringe if required
Two additional DISCARD blood collection tubes. One will be used to collect the discard sample and the other will be used to collect backflush.
Order labels from OneChart
Discard
3.Prepare Equipment and Environment
Explain procedure to patient/family.
Assemble vacutainer with access needle, sample tubes and/or blood gas syringe
Press the alarm silence to reduce nuisance alarms during blood sampling.
Blood sampling from an arterial line reduces patient discomfort from needle sticks, however, patients should be advised that they may feel a warm sensation in their extremity during line flushing.
4.Connect Blood Drawing System
Remove antiseptic. If no access camp present, scrub the hub for 15 seconds with 70% alcohol and 2% chlorhexidine swab. Wait 30 seconds dry time before accessing the port.
The Centre for Disease Control (CDC) recommends 70% alcohol or an or an iodophor for cleansing injection sites. Chlorhexidine adheres to provide prolonged gm positive antimicrobial properties.
Connect vactainer with sampling needle to luer-lock sampling port .
Begin with 3-way stopcock positioned with prong toward the sampling port (this is off to sampling port).
Stopcock off to sampling port with vacutainer connected.
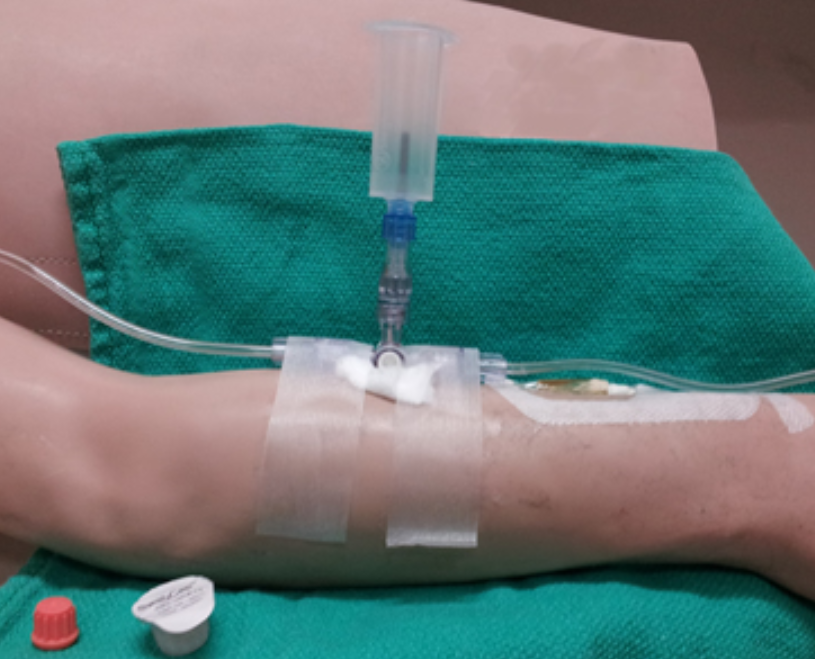
5.Collect Discard Sample (Artrial Lines)
Insert one of the DISCARD tubes into the vacutainer. Be careful to use tubes that will not be confused with actual blood samples.
Depress the blood tube to activate the vacuum.
Open up the flow of blood by turning the stopcock 90 degrees toward the flush system. This is open between the patient and sampling port.
Allow a minimum of 3 mL discard to be drawn from the arterial line.
Quickly turn the stopcock to 45 degrees (half-way between the patient and sampling port) when sufficient blood volume has been collected to avoid excess blood removal.
Remove the tube to release the vacuum and discard into the sharps container.
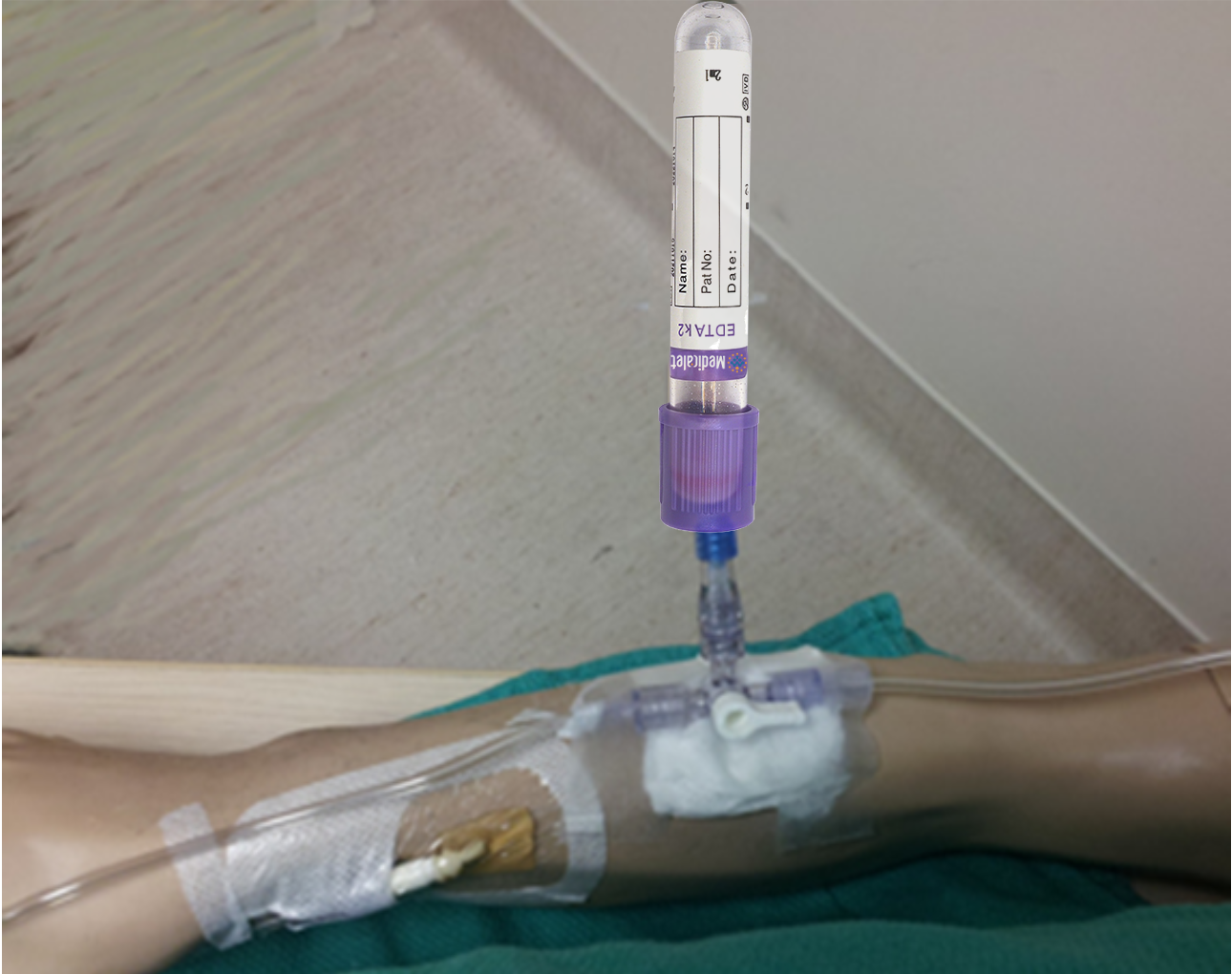
6.Collect Discard Sample (Venous Samples)
Assess all IVs that are running distal to the catheter during sampling.
All IVs that are running into any lumen of a multilumen or PICC catheter (including an introducer) must be off for blood sampling (except for blood gases).
A minimum discard sample of 5 ml is required when drawing blood samples from central venous lines due to longer lumen volume.
Peripheral IVs should not be used for blood sampling due to the high risk for hemolysis.
If IVs cannot be temporarily stopped, the patient should have an arterial line for lab sampling.
Infusions from distal peripheral lines or from any other port of a multilumen PICC or temporary venous catheter can dilute or contaminate a lab sample. These IVs should be turned off prior to sampling. If an infusion cannot be safely stopped during blood sampling, an alternative method for blood sampling is recommended.
Consider IV contamination for any patient with unusual electrolyte or lab values. TPN can significantly contaminate blood samples.
7.Collect Blood Samples to Prevent Dilution or Contamination with IV Fluids or Vaccum Tube Contents
Order of Draw
When drawing blood from an indwelling line, the INR/PTT should be drawn AFTER blood gases to prevent contamination of the PTT from the heparinized blood gas syringe.
Although we do not routinely heparinize our hemodynamic circuits anymore, any PTT drawn from a heparinized line should be drawn after at least a 5 ml discard.
The recommended order of blood tube collection is shown in Figure

8.Flush the Patient Catheter
When all of the desired specimens have been collected, turn the white prong on the stopcock toward the sampling port at 90 degrees (open to the patient and flush system).
Pull the flush device located below the transducer to activate the fast flush mechanism.
Flush until there is no visible evidence of blood.
Evaluate the waveform to ensure it has been restored.
9.Backflush the Stopcock
Connect the second extra syringe or blood tube to the sampling port.
Turn the stopcock so that the white prong points toward the patient's catheter. This is open between the flush and discard syringe.
Activate the flush device and back flush saline into the DISCARD tube or syringe.
Ensure all blood is cleared from the needleless access device.
Replace the needleless access device if residual blood remains after flushing
Connect a new luer lock antiseptic cap on the needleless access port.
Remove non-sterile gloves, perform hand hygiene.
tube
10.Label Specimens
Place labels on specimens at the bedside.
Verify that the label name and patient are correct.
Send blood samples to the lab in a biohazardous bag.
Years of experience in manufacturing laboratory consumables and medical products enables Medicalet to provide products of the highest quality and competitiveness. Through continuous innovation and practice, Medicalet has been recognized by more and more customers. If you are interested in Medicalet blood collection equipment, please feel free to contact us!
